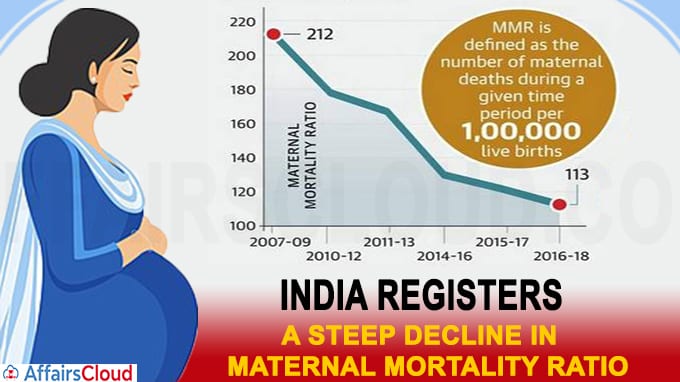
India has shown a steady decline in maternal mortality from 254 in every 100 000 live births in 2004 06 to 178 in every 100 000 live births in 2010 12.
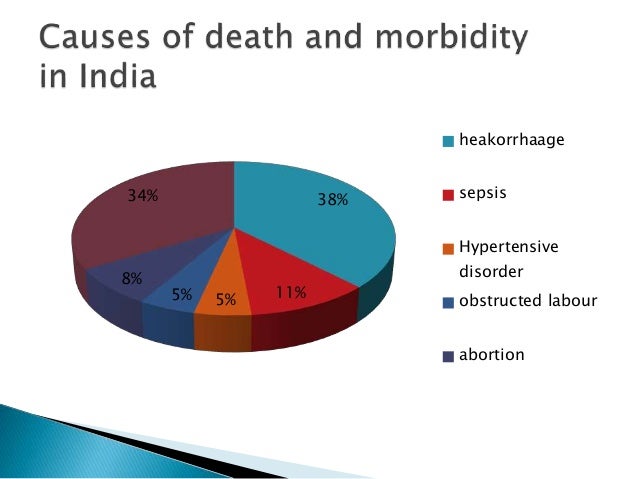
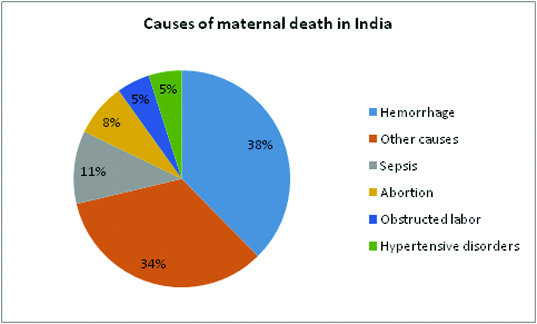
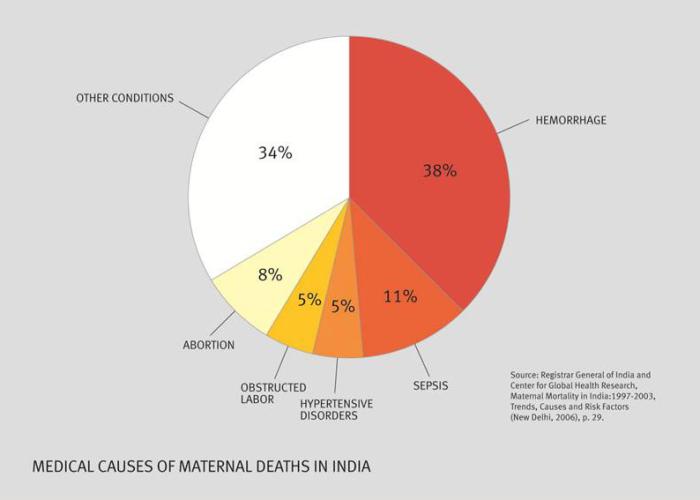
Causes of maternal mortality in india.
There was no difference in the major causes of maternal deaths between poorer and richer states.
By using both time series and cross sectional data this.
Most maternal deaths were attributed to direct obstetric causes 82.
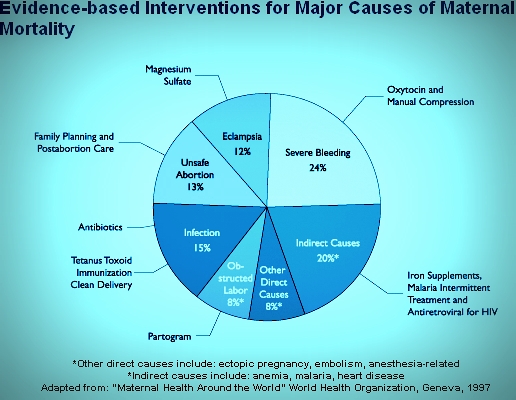
The major complications that account for nearly two thirds of all maternal deaths are severe bleeding mostly bleeding after childbirth infections usually after childbirth high blood pressure during pregnancy pre eclampsia and eclampsia complications from delivery and unsafe abortions.
Malaria and tuberculosis contributed to two deaths each the report said.
Antepartum haemorrhage caused six deaths 4 8 and 14 women 11 3 died from severe pre eclampsia eclampsia.
Two thirds of women died seeking some form of healthcare most seeking care in.
Maternal deaths were attributed to direct obstetric causes 82.
From 1980 2015 eclampsia is the cause of 1 5 of maternal deaths in india.
There was no difference in the major causes of maternal deaths between poorer and richer states.
Three quarters of maternal deaths were clustered in rural areas of poorer states although these regions have only half the estimated live births in india.
Summary studies on the causes of maternal mortality in india have focused on institutional deliveries and the association of socioeconomic and demographic factors with the decline in maternal mortality has not been sufficiently investigated.
Studies conducted in different parts of india and even in the global level have shown that hemorrhage is the most frequent cause of maternal mortality and eclampsia occupied the third position in.
There was no difference in the major causes of maternal deaths between poorer and richer states.
94 of all maternal deaths occur in low and lower middle income countries.
Three quarters of maternal deaths were clustered in rural areas of poorer states although these regions have only half the estimated live births in india.
There are various reasons for the death of women during their reproductive age 18 to 39 years that had been the cause of an increase in the maternal mortality rate.
Over that time the number of women who experience this disease has been the same but also there has been a slight reduction in the number of maternal death from the condition.
Every day in 2017 approximately 810 women died from preventable causes related to pregnancy and childbirth.
Most maternal deaths were attributed to direct obstetric causes 82.